Introduction
What Is Blepharitis
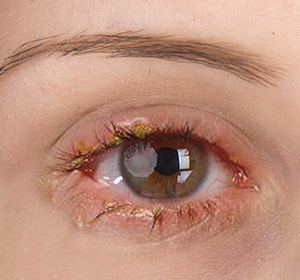
Blepharitis is a common condition characterised by inflammation of the eyelids, typically affecting both eyes along the edges of the eyelids. It causes redness, swelling, itchiness, and sometimes crusting, leading to discomfort and irritation. While blepharitis can be persistent and sometimes challenging to manage, it does not cause permanent damage to your eyesight. The condition often results from clogged or malfunctioning oil glands near the eyelashes and can be linked to other factors like dry eyes, infections, skin conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea, or allergic reactions. Proper eyelid hygiene and medical treatment can help control symptoms and improve eye comfort.
Causes and Risk Factors of Blepharitis
What Causes Blepharitis?
Blepharitis occurs due to inflammation often triggered by several factors, many of which affect the oil glands near the base of the eyelashes. These glands can become clogged or malfunction, leading to irritation and redness. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Clogged or malfunctioning oil glands near the eyelashes, disrupting normal tear film and causing inflammation
- Dry eyes, which can worsen eyelid irritation
- Infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses affecting the eyelid area
- Seborrheic dermatitis, a skin condition causing dandruff-like flakes around the eyes and scalp
- Rosacea, a facial redness disorder linked to blood vessel abnormalities
- Allergic reactions to eye makeup, contact lens solutions, or medications
- Eyelash mites or lice that irritate the eyelids
Understanding and managing these causes is important for controlling symptoms and preventing recurrence of blepharitis.
Types of Blepharitis
The Different Types of Blepharitis
Anterior Blepharitis
- Description:
Affects the front edge of the eyelid where the eyelashes are attached. Often caused by bacteria or scalp dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis). - Who it affects:
People with oily skin, dandruff, or bacterial infections. Can affect all ages. - Speed of progression:
Usually chronic, with flare-ups and remissions over months or years.
Posterior Blepharitis (Meibomian Gland Dysfunction)
Description:
Involves inflammation of the inner eyelid lining and blockage of the oil-producing Meibomian glands. Leads to poor tear quality and dry eyes.Who it affects:
Common in adults, especially those with skin conditions like rosacea or eczema.Speed of progression:
Chronic, progressive if untreated; may cause ongoing discomfort.
Infectious Blepharitis
Description:
Caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections leading to redness, swelling, and crusting.Who it affects:
Anyone can develop it; more common in those with compromised immunity or poor eyelid hygiene.Speed of progression:
Can worsen quickly if untreated, but usually resolves with proper treatment.
Seborrheic Blepharitis
Description:
Associated with seborrheic dermatitis affecting the eyelids, causing greasy flakes and redness.Who it affects:
People with dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis on other parts of the body.Speed of progression:
Often chronic, with periods of flare-ups and remission.
Early Signs & Symptoms
Common Symptoms of Blepharitis
Recognising early symptoms of blepharitis can help you seek timely treatment and avoid complications. Symptoms often develop gradually and may affect both eyes.
- Red, swollen eyelids
Eyelid edges appear inflamed and irritated. - Itchy or burning sensation
Persistent discomfort around the eyes. - Crusty or greasy eyelid margins
Flaking or buildup along the eyelashes, especially in the morning. - Watery or dry eyes
Excessive tearing or dryness due to poor tear film quality. - Frequent blinking or eye rubbing
Reflex response to irritation or discomfort. - Light sensitivity
Eyes may feel uncomfortable in bright light. - Blurred vision (temporary)
Caused by disrupted tear film or inflammation.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blepharitis
Blepharitis is diagnosed through a clinical eye examination using magnification to inspect the eyelids and lash line. If infection is suspected, your doctor may take a swab for testing. Treatment often begins with daily eyelid cleaning and warm compresses to reduce inflammation. In more persistent cases, antibiotic or steroid eye drops may be prescribed. With consistent care, symptoms can usually be managed effectively.
Why Timely Diagnosis Matters
Chronic Lid Inflammation Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Blepharitis is rarely sight-threatening, but if left untreated, it can lead to persistent discomfort, recurring infections, and even long-term eye surface damage. Early diagnosis helps manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life.
Prompt diagnosis ensures your ophthalmologist can:
- Rule out underlying infections or allergies
- Prevent complications like styes, dry eyes, or corneal damage
- Recommend appropriate lid hygiene and medical treatments
- Identify if blepharitis is linked to other skin or eye conditions
- Provide long-term care to reduce flare-ups and relapses
Consistent care and early management make blepharitis more manageable and reduce the likelihood of chronic irritation or visual disturbance.
Continue Learning About Other Eye Conditions
Other Eye Conditions
The eyes are the most complex sensory organ in our bodies. The eyes provide vision by recording images of our surroundings that the brain will interpret. Although the eye measures only about an inch...
Worried About Your Vision?
Schedule a consultation with Mr. Mo Majid to evaluate your eye health.
Quick Answers About Blepharitis
Is blepharitis contagious?
No, blepharitis is not contagious. While it may be triggered by bacteria, it cannot be spread from person to person.
Can blepharitis be cured?
There’s no permanent cure, but symptoms can be well-managed with regular eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and prescribed treatments when needed.
Will blepharitis affect my vision?
Blepharitis typically does not cause permanent vision loss. However, untreated cases may cause blurry vision, dry eyes, or corneal irritation.
Should I stop wearing contact lenses?
If you have active symptoms, it’s advisable to stop wearing contacts temporarily. Your ophthalmologist will let you know when it’s safe to resume.